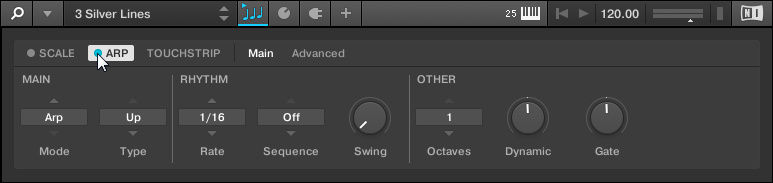
Using Scales and the Arpeggiator
With Play Assist, Komplete Kontrol gives you new and inspiring ways to perform using the Scale engine and the Arpeggiator. Map your keyboard to any one of over 100 different scales and modes, play chords with one finger, effortlessly create expressive arpeggios, and more.
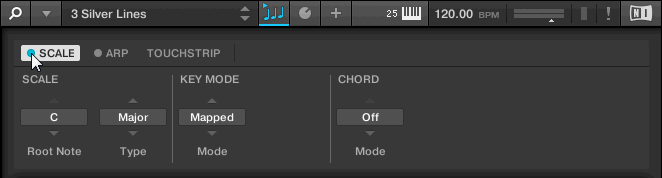
The Perform panel lets you access all the parameters related to the Scale engine and the Arpeggiator.
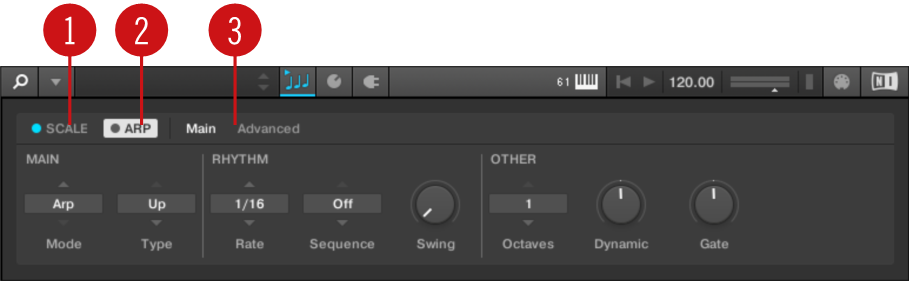
SCALE: Clicking the round button left of SCALE switches the Scale engine on or off. Clicking the SCALE label displays the Scale engine’s parameters. See Scale for details.
ARP: Clicking the round button left of ARP switches the Arpeggiator on or off. Clicking the ARP label displays the Arpeggiator’s parameters. See Arpeggiator for details.
Parameter pages: If multiple pages of parameters are available, you can switch between them here.
Scale
Scale maps the notes you play using your keyboard or sequencer to the closest notes contained in the selected scale. It features a vast amount of different scales that you can use to play your instruments. In Chord mode, you can use the scales to generate chords from single notes. Combined with the Arpeggiator, you can play scales automatically with a variety of different motives and rhythms.
Activating Scale
Editing Scales and Chords
You can tailor the scales and chords to your needs using the Scale engine parameters.
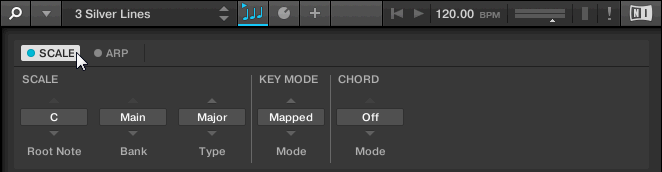
You can select the scale to be mapped to the keys of the keyboard and set its root note by using the SCALE parameters Root Note, Bank, and Type. For more information, refer to Scale Parameters.
You can define how the selected scale is mapped to the keys of the keyboard by using the KEY MODE parameter Mode. For more information, refer to Key Mode Parameter.
You can automatically generate custom chords while playing on the keyboard by using the CHORD parameters Mode, Type, and Position. For more information, refer to Chord Parameters.
Scale Parameters
The SCALE parameters Root Note, Bank, and Type allow you to select the scale to be mapped to the keys of the keyboard and set its root note.
Scale Root Note
The first SCALE parameter is Root Note. Setting the root note of a scale means deciding what key the scale will begin with. The following notes of the scale depend on which scale pattern you select with the SCALE Type parameter (see below). You can transpose any scale pattern up or down by selecting a different Root Note.
The Root Note setting includes the following values:
C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, B
Scale Bank and Type
The second and third SCALE parameters from the left are Bank and Type. Use them to decide the scale pattern according to which the notes will be mapped onto the keys of the keyboard. Each Bank consists of 15 thematically related scales, which can be selected by using the Type control.
For example, using the default Root Note value C combined with the default Type Major from the default Bank Main, you get the scale C major, which spans over one octave and contains the notes C, D, E, F, G, A, and B (followed by C again). If instead you select G as your Root Note, the G major scale contains the notes G, A, B, C, D, E, and F♯ (followed by G again). You will notice that the distance between each note follows the same pattern of “whole step–whole step–half step–whole step–whole step–whole step–half step,” which is the pattern of the Major scale.
If you are triggering an Instrument via an incoming MIDI pattern from the DAW, the notes of the MIDI pattern will be mapped onto the closest keys belonging to the selected Type. This means that, for example (with Root Note set to C) a MIDI pattern consisting of the notes C-D-D♯ will be played back as such if Type is set to Chromatic from Bank Main, but instead as C-D-E if Type is set to Major.
Note
The actual keys triggering the scale notes, as well as the behavior of inactive keys (unlit LEDs) depend on the KEY MODE Mode parameter (Knob 4).
The following scales are available:
Main Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Chromatic | Main | Chrom | 1 ♭2 2 ♭3 3 4 ♭5 5 ♭6 6 ♭7 7 |
Major | Main | Major | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Minor | Main | Minor | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Harm Min | Main | Harm Min | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Maj Pent | Main | Maj Pent | 1 2 3 5 6 |
Min Pent | Main | Min Pent | 1 ♭3 4 5 ♭7 |
Blues | Main | Blues | 1 ♭3 4 ♯4 5 ♭7 |
Japanese | Main | Japanese | 1 2 ♭3 5 ♭6 |
Freygish | Main | Freygish | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Hungarian Min | Main | Hung Min | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 ♭6 7 |
Arabic | Main | Arabic | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Altered | Main | Altered | 1 ♭2 ♯2 3 ♯4 ♭6 ♭7 |
Whole Tone | Main | WH Tone | 1 2 3 ♯4 ♯5 ♭7 |
H-W Dim | Main | H-W Dim | 1 ♭2 ♯2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
W-H Dim | Main | W-H Dim | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♯4 ♯5 6 7 |
Modes Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Ionian | Modes | Ionian | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Dorian | Modes | Dorian | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 6 ♭7 |
Phrygian | Modes | Phrygian | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Lydian | Modes | Lydian | 1 2 3 ♯4 5 6 7 |
Mixolydian | Modes | Mixolyd | 1 2 3 4 5 6 ♭7 |
Aeolian | Modes | Aeolian | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Locrian | Modes | Locrian | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Ionian b2 | Modes | Ion b2 | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Dorian b5 | Modes | Dor b5 | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♭5 6 ♭7 |
Harm Phryg | Modes | Har Phry | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Phryg Major | Modes | Phry Maj | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 6 7 |
Lydian b3 | Modes | Lyd b3 | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 6 7 |
Major Locrian | Modes | Maj Loc | 1 2 3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Minor Locrian | Modes | Min Loc | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Super Locrian | Modes | Sup Loc | 1 ♭2 ♭3 ♭4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Jazz Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Lydian ♭7 | Jazz | Lyd ♭7 | 1 2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Altered | Jazz | Altered | 1 ♭2 ♯2 3 ♯4 ♭6 ♭7 |
Diminished | Jazz | Diminshd | 1 ♭2 ♯2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Mixo b13 | Jazz | Mix b13 | 1 2 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Mixo b9 b13 | Jazz | Mixb9b13 | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Lydian ♭7 b2 | Jazz | Lyd ♭7b2 | 1 ♭2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Bebop | Jazz | Bebop | 1 2 3 4 5 6 ♭7 7 |
Whole Tone | Jazz | Whole Tn | 1 2 3 ♯4 ♯5 ♭7 |
Blues Maj | Jazz | Blues Ma | 1 2 ♭3 3 5 6 |
Blues Min | Jazz | Blues Mi | 1 ♭3 4 ♯4 5 ♭7 |
Blues Combined | Jazz | BluesCmb | 1 2 ♭3 3 4 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Lydian #5 | Jazz | Lyd #5 | 1 2 3 ♯4 ♯5 6 7 |
Jazz Minor | Jazz | Jazz Mi | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 6 7 |
Half Dim | Jazz | Half Dim | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Augmented | Jazz | Augmentd | 1 ♭3 3 5 ♯5 7 |
World Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Hungarian Min | World | Hung Min | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 ♭6 7 |
Hungarian Maj | World | Hung Maj | 1 ♯2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Neapolitan | World | Neapoltn | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Spanish | World | Spanish | 1 ♭2 ♭3 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Greek | World | Greek | 1 2 ♭3 ♭4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Jewish 1 | World | Jewish 1 | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Jewish 2 | World | Jewish 2 | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Indian 1 | World | Indian 1 | 1 ♭2 ♭3 ♯4 5 ♭6 7 |
Indian 2 | World | Indian 2 | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 6 7 |
Indian 3 | World | Indian 3 | 1 ♭2 2 4 5 ♭6 6 |
Indian 4 | World | Indian 4 | 1 ♯2 3 4 5 ♯6 7 |
Mid East 1 | World | M East 1 | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Mid East 2 | World | M East 2 | 1 ♭2 3 4 ♭5 ♭6 7 |
Mid East 3 | World | M East 3 | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 ♭5 6 ♭7 |
Mid East 4 | World | M East 4 | 1 ♭2 3 4 ♭5 6 ♭7 |
5-Tone Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Penta I | 5-Tone | Pent I | 1 2 3 5 6 |
Penta II | 5-Tone | Pent II | 1 2 4 5 ♭7 |
Penta III | 5-Tone | Pent III | 1 ♭3 4 ♭6 ♭7 |
Penta IV | 5-Tone | Pent IV | 1 2 4 5 6 |
Penta V | 5-Tone | Pent V | 1 ♭3 4 5 ♭7 |
Hirajoshi | 5-Tone | Hira | 1 2 ♭3 5 ♭6 |
Insen | 5-Tone | Insen | 1 ♭2 4 5 ♭7 |
Kokin Joshi | 5-Tone | Kokin | 1 2 4 5 ♭6 |
Akebono | 5-Tone | Akebono | 1 2 ♭3 5 6 |
Ryukuan | 5-Tone | Ryukuan | 1 3 4 5 7 |
Abhogi | 5-Tone | Abhogi | 1 2 ♭3 4 6 |
Bhupkali | 5-Tone | Bhupkali | 1 2 3 5 ♭6 |
Hindolam | 5-Tone | Hindolam | 1 ♭3 4 ♭6 ♭7 |
Bhupalam | 5-Tone | Bhupalam | 1 ♭2 ♭3 5 ♭6 |
Amritavarshini | 5-Tone | Amrita | 1 3 ♯4 5 7 |
Modern Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Octatonic | Modern | Octatonc | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♯4 ♯5 6 7 |
Acoustic | Modern | Acoustic | 1 2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Augmented | Modern | Augmentd | 1 ♭3 3 5 ♯5 7 |
Tritone | Modern | Tritone | 1 ♭2 3 ♭5 5 ♭7 |
Leading Wh Tone | Modern | Lead Wh | 1 2 3 ♯4 ♯5 ♯6 7 |
Enigmatic | Modern | Enigmatc | 1 ♭2 3 ♯4 ♯5 ♯6 7 |
Scriabin | Modern | Scriabin | 1 2 3 ♯4 6 ♭7 |
Tcherepnin | Modern | Tcherepn | 1 ♯1 ♯2 3 4 5 ♯5 6 7 |
Messiaen I | Modern | Mes I | 1 2 3 ♯4 ♯5 #6 |
Messiaen II | Modern | Mes II | 1 ♭2 ♯2 3 ♯4 5 6 ♭7 |
Messiaen III | Modern | Mes III | 1 2 ♭3 3 ♯4 5 ♭6 ♭7 7 |
Messiaen IV | Modern | Mes IV | 1 ♭2 2 4 ♯4 5 ♭6 7 |
Messiaen V | Modern | Mes V | 1 ♭2 4 ♯4 5 7 |
Messiaen VI | Modern | Mes VI | 1 2 3 4 ♯4 ♯5 ♯6 7 |
Messiaen VII | Modern | Mes VII | 1 ♭2 2 ♭3 4 ♯4 5 ♭6 6 7 |
Major Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Natural | Major | Natural | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Lydian | Major | Lydian | 1 2 3 ♯4 5 6 7 |
Mixolydian | Major | Mixolyd | 1 2 3 4 5 6 ♭7 |
Major Minor | Major | Maj Min | 1 2 3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Harmonic Major | Major | Har Maj | 1 2 3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Dbl Har Major | Major | Dbl Maj | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Neapolitan Maj | Major | Nea Maj | 1 ♭2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Major Locrian | Major | Maj Loc | 1 2 3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Blues Major | Major | Blues Ma | 1 2 ♭3 3 5 6 |
Bebop Major | Major | Bebop Ma | 1 2 3 4 5 ♯5 6 7 |
Hexa 1 | Major | Hexa 1 | 1 2 3 5 6 7 |
Hexa 2 | Major | Hexa 2 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Penta 1 | Major | Penta 1 | 1 2 3 5 6 |
Penta 2 | Major | Penta 2 | 1 3 4 5 7 |
Penta 3 | Major | Penta 3 | 1 3 5 6 7 |
Minor Scales
Scale | Bank | Type | Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
Natural | Minor | Natural | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Dorian | Minor | Dorian | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 6 ♭7 |
Phrygian | Minor | Phrygian | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Minor Major | Minor | Min Maj | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 6 7 |
Harmonic Minor | Minor | Har Min | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Dbl Har Minor | Minor | Dbl Min | 1 2 ♭3 ♯4 5 ♭6 7 |
Neapolitan Min | Minor | Nea Min | 1 ♭2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 7 |
Minor Locrian | Minor | Min Loc | 1 2 ♭3 4 ♭5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Blues Min | Minor | Blues Mi | 1 ♭3 4 ♯4 5 ♭7 |
Bebop Minor | Minor | Bebop Mi | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 ♭7 7 |
Hexa 1 | Minor | Hexa 1 | 1 2 ♭3 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Hexa 2 | Minor | Hexa 2 | 1 2 ♭3 4 5 ♭6 |
Penta 1 | Minor | Penta 1 | 1 2 ♭3 5 ♭6 |
Penta 2 | Minor | Penta 2 | 1 ♭3 4 5 ♭7 |
Penta 3 | Minor | Penta 3 | 1 ♭3 5 ♭6 ♭7 |
Key Mode Parameter
The KEY MODE Mode menu consists of the following three modes, which are described in detail below:
Guide
Mapped (default value)
Easy
Easy Mode
In Easy mode, the notes of the selected scale are mapped to the keyboard so that any scale can be played using the white keys of the keyboard only. The black keys are inactive and pressing them will not trigger any other notes.
Notice
Selecting the 12-step chromatic scale in KEY MODE Easy maps the keys in the same way as in the Mapped mode.
The Root Note is always mapped to the middle C key (commonly called C3). If the selected scale consists of seven notes, it matches the seven white keys of a single octave on the keyboard. In this case, the Root Note coincides with the key C across all octaves of the keyboard. If instead the selected scale consists of more or less than seven notes, it does not match the seven white keys of a single octave on the keyboard and the Root Note is shifted throughout adjacent octaves accordingly.
For two examples of the Easy mode mappings in Major and Minor, refer to below.
Scale Type | Key Mappings in Easy Mode | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
White keys: | C3 | D3 | E3 | F3 | G3 | A3 | B3 |
Major | |||||||
Corresponding mappings: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Example with root note C: | C | D | E | F | G | A | B |
Minor | |||||||
Corresponding mappings: | 1 | 2 | ♭3 | 4 | 5 | ♭6 | ♭7 |
Example with root note C: | C | D | ♭E | F | G | ♭A | ♭B |
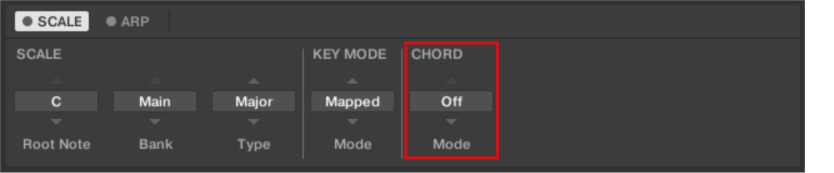
Chord Parameters
The CHORD parameters Mode, Type and Position allow you to define the chord to be played using the Chord function.
Chord Mode
The first CHORD parameter is Mode. Use it to generate chords from single notes, either from the keyboard or from incoming MIDI notes from the DAW.
CHORD Mode has one inactive (Off) and two active states, which are described in detail below:
Off
Harmonizer
Chord Set
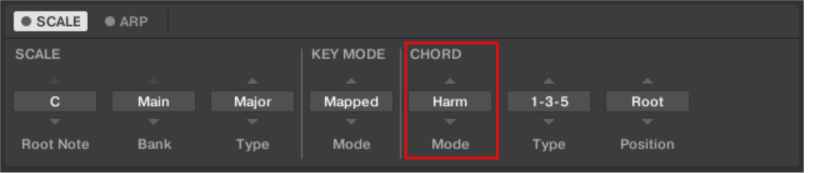
Harmonizer
If CHORD Mode is set to Harm (Harmonizer), the CHORD Type menu allows you to specify the interval of notes in the selected SCALE Type that will constitute the chord: For example, a triad in the form of the root note, the third note, and the fifth note (CHORD Type value 1-3-5).
Chord Set
If CHORD Mode is set to Chord Set (Chord Set), the CHORD Type menu allows you to choose from a selection of major and minor chords depending on the current Root Note.
Notice
The SCALE Type and KEY MODE Mode parameters are not available when CHORD Mode is set to Chord Set.
Chord Type
The second CHORD parameter is Type. Use it to select the chord that will be generated from a single note used as input.
The available CHORD Type values depend on whether CHORD Mode is set to Harmonizer or Chord Set, as described in detail below.
CHORD Type, CHORD Mode Set to Harmonizer
If CHORD Mode is set to Harmonizer, then CHORD Type will offer you a selection of individual notes present in the selected SCALE Type. This means that for all scales except the 12-tone Chrom scale (chromatic scale, refer to further below), you can select the interval of notes that will make up your chord.
When CHORD Mode is set to Harm, the CHORD Type setting includes the following values:
Chord Type | Interval Added to Played Note |
|---|---|
Octave | Octave |
1-3 | 3rd |
1-5 | 5th |
1-3-5 | 3rd and 5th |
1-4-5 | 4th and 5th |
1-3-5-7 | 3rd, 5th and 7th |
1-4-7 | 4th and 7th |
CHORD Type, CHORD Mode Set to Chd Set
If CHORD Mode is set to Chord Set and, for example, the Root Note is set to C, then the CHORD Type menu presents you with a list of selectable chords. Values are, e.g., Maj 4 and Min 7, which would generate a major and minor chord, respectively, both using C as the chord’s root note.
When CHORD Mode is set to Chord Set, the CHORD Type setting includes the following values:
Maj 1, Maj 2, Maj 3, Maj 4, Maj 5, Maj 6, Maj 7, Maj 8, Min 1, Min 2, Min 3, Min 4, Min 5, Min 6, Min 7, Min 8
CHORD Type and the Chromatic Scale
The Chrom (chromatic) scale consists of every semitone in an octave. This means that when you play every white key and every black key of an octave up or down, you are playing the 12-step chromatic scale. Since all semitones of an octave are present in the scale, you can use all keys to form chords. In turn, selecting Chrom as SCALE Type means that you can select virtually any CHORD Type. The following chords are available and can be generated:
Chord Type | Semitones Added above Played Note |
|---|---|
Octave | 12 |
Perf 4 (Perfect 4) | 5 |
Perf 5 (Perfect 5) | 7 |
Major | 4 and 7 |
Minor | 3 and 7 |
Sus 4 (Suspended 4) | 5 and 7 |
Maj 7 (Major 7) | 4, 7 and 11 |
Min 7 (Minor 7) | 3, 7 and 10 |
Dom 7 (Dominant 7) | 4, 7 and 10 |
Dom 9 (Dominant 9) | 4, 7, 10 and 14 |
Min 7 ♭5 (Minor 7 ♭5) | 3, 6 and 10 |
Dim 7 (Diminished 7) | 3, 6 and 9 |
Aug (Augumented) | 4 and 8 |
Quartal | 5, 10 and 15 |
Trichord | 5 and 11 |
ChordPosition
The third CHORD parameter is Position. Use it to spread the notes of a chord generated from a single note and to aid a more musical transition between chords.
The Position parameter is available when CHORD Type is set to Harmonizer or Chord Set and includes the following values:
Position | Description |
|---|---|
Root | The root position of the selected chord is always played. |
-1 to -8 | Decreasing Position with negative values moves the highest note of the current chord down by an octave, this inverts the chord to a lower position in the selected scale. |
+1 to +8 | Increasing Position with positive values moves the lowest note of the current chord up by an octave, this inverts the chord to a higher position in the selected scale. |
Auto | This provides a more human feel in the transition from one chord to another. The notes used to form each chord are automatically selected to provide the best inversion. |
Arpeggiator
The Arpeggiator enables you to automatically generate musical sequences according to the notes you play using your keyboard or sequencer. It features a vast amount of different motives and rhythms that you can use to play your instruments. Combined with the Scale engine, you can play motives and rhythms while also constraining the notes to the selected scale.
Activating the Arpeggiator
Playing the Arpeggiator
Editing the Arpeggiator
The Arpeggiator parameters give you many possibilities to shape your own note sequences.
You can switch between Arp and Note Repeat mode and change the playback direction of the arpeggiator sequence by using the MAIN parameters Mode and Type. For more information, refer to Main Parameters.
You can create interesting rhythms for the arpeggiator sequence by using the RHYTHM parameters Rate, Sequence, and Swing. For more information, refer to Rhythm Parameters.
You can change the range of available notes for the arpeggiator sequence, as well as their velocity and length, by using the OTHER parameters Octaves, Dynamic, and Gate. For more information, refer to Other Parameters.
You can explore alternative versions of the same arpeggiator sequence by using the ADVANCED parameters Retrigger, Repeat, Offset, and Inversion. For more information, refer to Advanced Parameters.
You can change the range of keys that trigger the arpeggiator sequence by using the RANGE parameters Min. Key and Max. Key. For more information, refer to Range Parameters.
You can latch the playback of the arpeggiator sequence by using the HOLD On/Off parameter. For more information, refer to Hold Parameter.
Main Parameters
The MAIN parameters Mode and Type allow you to switch between Arp and Note Repeat mode and change the playback direction of the arpeggiator sequence.
Main Mode
The first MAIN parameter is Mode. lt lets you select either Arp or Note Repeat. Depending on your selection, a different set of Arpeggiator parameters will be available for further editing.
The Mode setting consists of the following two modes:
Arp mode, which generates arpeggiator sequences based on chords you play on the keyboard, or the output of the Scale engine. With the Arpeggiator switched on and Mode set to Arp, any chord you created using the Scale engine will play as an arpeggiated note sequence. In this case, you only need to press one key on the keyboard to hear the arpeggiated notes play out according to the selected scale.
Note Repeat mode, which deactivates the Arpeggiator and instead repeats whichever note is input until Komplete Kontrol receives a MIDI note-off message. Use the parameters Rate, Swing, and Gate to change the rhythm of the repeats.
Main Type
The second MAIN parameter, Type, is only available in Arp mode. It sets the sequential order of the arpeggiated notes. Choose whether your arpeggiated chord should be played from the root note and up, the other way around, or even simultaneously. Selecting Order Played will play back the notes in the order you pressed down the corresponding keys on the keyboard. Automating the Type parameter in the DAW can create interesting variations and textures.
The Type setting includes the following values:
Up, Down, Up & Down, Order Played, Chord
Rhythm Parameters
The RHYTHM parameters Rate, Sequence, and Swing allow you to create interesting rhythms for the arpeggiator sequence.
Rhythm Rate
The first RHYTHM parameter, Rate, is available in both Arp and Note Repeat mode. It sets the beat of the Arpeggiator in relation to global tempo in musical values, ranging from 1/1 to 1/128. All note values (except 1/1 and 1/128) are available as basic notes, dotted notes, and triplets. Dotted notes are 1.5 times longer than the corresponding basic notes. Triplets are 2/3 the duration of their corresponding basic notes, so that e.g., three 1/4 notes are equal in duration to two basic 1/4 notes.
The Rate setting includes the following values:
1/1
1/2 Dotted (1/2 D)
1/1 Triplet (1/1 T)
1/2
1/4 Dotted (1/4 D)
1/2 Triplet (1/2 T)
1/4
1/8 Dotted (1/8 D)
1/4 Triplet (1/4 T)
1/8
1/16 Dotted (1/16 D)
1/8 Triplet (1/8 T)
1/16
1/32 Dotted (1/32 D)
1/16 Triplet (1/16 T)
1/32
1/64 Dotted (1/64 D)
1/32 Triplet (1/32 T)
1/64
1/128 Dotted (1/128 D)
1/64 Triplet (1/64 T)
1/128
Rhythm Sequence
The second RHYTHM parameter, Sequence, is only available in Arp mode. It gives you a way of adding interesting rhythms to your arpeggiated notes. Select one of eight different sequences and apply it to the arpeggiator sequence you are playing. Combine Sequence with the Rate parameter to create a huge variety of rhythms at different tempos. If Rate is set to a basic or dotted value, then Sequence applies a 16-step sequencer to the notes. If Rate is instead set to a triplet value, then Sequence applies a 12-step sequencer to the notes.
You can switch sequences in real time during playback. For example, if sequence 1 is running and you instead select sequence 2 after the fourth MIDI note in a pattern has been played back, then sequence 2 starts when the fifth MIDI note in the pattern is played back.
The Sequence setting includes the following values:
Off, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Rhythm Swing
The third RHYTHM parameter, Swing, is available in both Arp and Note Repeat mode. Adding Swing to your note sequence can make it feel less quantized and sound more natural. Swing works by introducing a delay to every second note in a sequence. Doing so often adds a certain groove to the music.
Swing lets you set a value between 0% and 100%:
Set a value of 0% to play the note sequence without swing.
Increase the Swing value to add swing by delaying every second note. The delay length is a percentage of the current step size.
Using Swing in combination with the Gate parameter adds further variations in note duration. For example, if Gate is set to 100%, Komplete Kontrol sends a MIDI note-off message before each note and plays back the sequence legato. If Gate is set to values larger or smaller than 100%, then notes will be scaled after the value of the Swing parameter has been applied, leaving the groove intact.
Other Parameters
The OTHER parameters Octaves, Dynamic, and Gate allow you to change the range of available notes for the arpeggiator sequence, as well as their velocity and length.
Other Octaves
The first OTHER parameter, Octaves, is only available in Arp mode. It lets you decide the range of the arpeggiator sequence. You can choose to play back your sequence within the octave of only the keys you pressed on the keyboard, or you can select up to eight octaves and let the corresponding notes of your chord or scale be played back in as many octaves.
Depending on the settings you have made to the Type parameter, the octaves played back can be above (e.g., Up), below (e.g., Down) or both above and below (Up & Down) the pressed keys.
The Octaves setting includes the following values:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Other Dynamic
The second OTHER parameter, Dynamic, is only available in Arp mode. It reads the velocity of the input (a key you pressed on the keyboard or an incoming MIDI note from the DAW) and scales it by the factor you set with the Dynamic parameter. The scaling is applied per note. The velocity of each played note is taken and multiplied by the value set with the Dynamic parameter.
Dynamic lets you set a value between 1.0% and 200.0%.
Other Gate
The third OTHER parameter, Gate, is available in both Arp and Note Repeat mode. It lets you decide the length of the notes in your sequence. Setting a value between 1% and 99% makes the duration of the notes shorter than they otherwise would be. Setting a value between 101% and 200% instead elongates the duration of the notes.
Gate lets you set a value between 1.0 % and 200.0 %.
Advanced Parameters
The ADVANCED parameters Retrigger, Repeat, Offset, and Inversion allow you to explore alternative versions of the same arpeggiator sequence.
Advanced Retrigger
The first ADVANCED parameter, Retrigger, is only available in Arp mode. Retrigger sets a number of steps in the arpeggiator sequence after which the sequence restarts its cycle, regardless of the number of pitches in the sequence.
For example:
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 5 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5) and Retrigger is set to 3, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - repeat.
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 5 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5) and Retrigger is set to 8, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 1 - 2 - 3 - repeat.
Rests in a Sequence are treated as steps:
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of 6 pitches, the Sequence is 1 - 2 - 3 - rest - 4 - 5 - 6 – rest, and Retrigger is set to 5, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - rest - 4 -repeat.
Advanced Repeat
The second ADVANCED parameter, Repeat, is only available in Arp mode. Repeat sets a number by which each step in the arpeggiator sequence is repeated.
For example:
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 3 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3) and Repeat is set to 3, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 1 - 1 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 3 - 3 - 3 - repeat.
Advanced Offset
The third ADVANCED parameter, Offset, is only available in Arp mode. Offset sets a number by which the steps in the arpeggiator sequence are shifted in the cycle.
For example:
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 5 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5) and Offset is set to 0, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - repeat.
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 5 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5) and Offset is set to +1, the Arpeggiator output is 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 1 - repeat.
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 5 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5) and Offset is set to -1, the Arpeggiator output is 5 - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - repeat.
Advanced Inversion
The fourth ADVANCED parameter, Inversion, is only available in Arp mode. Inversion adds inverted alternations of the arpeggiator sequence to the cycle.
For example:
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 3 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3), Type is set to Up, and Inversion is set to 0, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - repeat.
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 3 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3), Type is set to Up, and Inversion is set to 1, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 - 2 - 3 - repeat.
If the arpeggiator sequence consists of a 3 note cycle (1 - 2 - 3), Type is set to Up, and Inversion is set to 2, the Arpeggiator output is 1 - 2 - 3 – (2 - 3 - 1 octave up) - (3 - 1 - 2 octave up) - repeat.
Range Parameters
The RANGE parameters Min. Key and Max. Key allow you to change the range of keys that trigger the arpeggiator sequence.
Range Min. Key
The first RANGE parameter, Min. Key, is only available in Arp mode. Min. Key sets the lowest key that can be used as an input for the arpeggiator sequence.
Tip
The Arpeggiator can still generate pitches below the Min. Key setting.
Range Max. Key
The second RANGE parameter, Max. Key, is only available in Arp mode. Max. Key sets the highest key that can be used as an input for the arpeggiator sequence.
Tip
The Arpeggiator can still generate pitches above the Max. Key setting.
Hold Parameter
The HOLD On/Off parameter is available in both Arp and Note Repeat mode. The Hold feature allows you to latch the notes played by the Arpeggiator. When HOLD On/Off is active, the Arpeggiator will continuously play a sequence according to the last pressed keys on the keyboard.
Pressing any key while HOLD On/Off is active will set a new sequence.
To stop the Arpeggiator playback, deactivate HOLD On/Off.
Tip
Alternatively, you can switch the Arpeggiator completely off to stop playback. When you switch the Arpeggiator back on, HOLD On/Off will still be active and you can continue to play latched note sequences with the Arpeggiator.